Manually transcribing audio is a laborious task. For the average person, it can take around four hours to transcribe just one hour of audio. Professional transcriptionists can do the job within two to three hours. However, their speed will also depend on the quality of the audio file, background noises, and a lot of other factors.
The burden of administrative tasks like manual transcription, is largely felt in the healthcare industry. In the 2019 Medscape National Physician Burnout survey, for instance, 59% of physicians said paperwork contributes the most to their feelings of burnout.
The relatively new technology of speech recognition software is a promising tool that aims to solve this pain point. The computer-based transcription service it offers takes away the human component of typing text, freeing up employees to do other critical tasks. And with the voice and speech recognition market poised to grow into a $31.82 billion industry by 2025, more industries will benefit from its adoption.

List of Best Voice Recognition Software
- What is Voice Recognition Software?
- Top Voice Recognition Software
- How Voice Recognition Software Works
- Voice Recognition Software Features
- Voice Recognition Software Benefits
- Types of Voice Recognition Software
- Voice Recognition Software Trends
- Potential Issues with Voice Recognition Software
- Factors to Consider when Looking for Voice Recognition Software
What is Voice Recognition Software?
Voice recognition software is a tool that makes it easier and faster to convert audio to text. Coupled with the latest advances in machine learning and artificial intelligence, modern voice recognition software is capable of giving highly accurate results. In a corporate setting, team members can use it to create documents without using a mouse and keyboard. On the other hand, businesses with large volumes of customer interactions can use it to create human-like engagements. As such, it is a great tool to have for businesses looking to move away from manual transcription. Find out more about voice recognition software by reading about the top providers below.
List of Best Voice Recognition Software
- Dragon Professional. The Dragon Professional speech recognition software allows busy professionals to create documents with their voice or voice overs. The software adapts to your voice and environment to improve accuracy as you dictate.
- Microsoft Azure Speech Services. This service lets developers add natural-sounding speech-to-text capabilities to apps. It also provides speech translation and batch transcription of call center recordings.
- Express Scribe. Express Scribe is an audio playback software for audio and video transcription. The user can use hotkeys or foot pedals to make transcription work faster.
- Microsoft Azure Speaker Recognition. This software allows businesses to verify a customer’s identity through voice. Voice can be used as an additional authentication method or to recognize who is speaking from a group of enrolled speakers.
- AssemblyAI Speech-to-Text API. This top-rated voice recognition software uses the latest in deep learning technology to provide AI-powered solutions. With it, users can easily transcribe audio or video from any file format.
- Amazon Transcribe. Using automatic speech recognition, Amazon Transcribe can provide fast and precise speech-to-text conversion. It can be used in transcribing calls or generating closed captions and subtitles.
- IBM Watson Speech to Text. This cloud-native solution uses machine learning to provide custom speech-to-text conversion for business use. You can create custom language and acoustic models to recognize jargon, regional dialects, and more.
- Google Cloud Speech-to-Text. Speech-to-Text enables developers to incorporate Google speech recognition into apps. It can detect over 120 languages and variants and show text transcriptions in real-time.
- Bighand Dictate. Bighand Dictate can transcribe recording in real-time with 99% accuracy. Through digital dictation, employees save time spent on unnecessary admin work.
- Microsoft Azure Custom Speech. This service lets you customize your speech-to-text model for improved quality. With it, apps can recognize jargon or speaker utterances despite background noise.
How Voice Recognition Software Works
Voice recognition software works by capturing your voice, analyzing it, and executing the command for the desired result.
The process begins when you speak into a microphone, whether from your smartphone, computer, or another device. The software then converts raw audio waveforms into text by splicing words into phonemes or the smallest unit of sound. The software identifies which phonemes were spoken and combines them to recognize the words you have spoken. It also looks at other words from its vocabulary database to understand what was said.
Once the speech-to-text conversion is done, the software analyzes the contents of the utterance. It uses natural language processing (NLP) to come up with an appropriate response. If a spoken response from your device is needed, the software then proceeds to text-to-speech conversion. As a result, you’ll hear a response, as when Alexa tells you what the weather is today. Other times, the software carries out a task instead of a verbal response. For example, when you ask the Dragon Professional software “What can I say?” it will open up a menu of command within the program you’re using.
Voice recognition may involve an enrollment process. This involves the user speaking a few lines for the software to create a voiceprint.
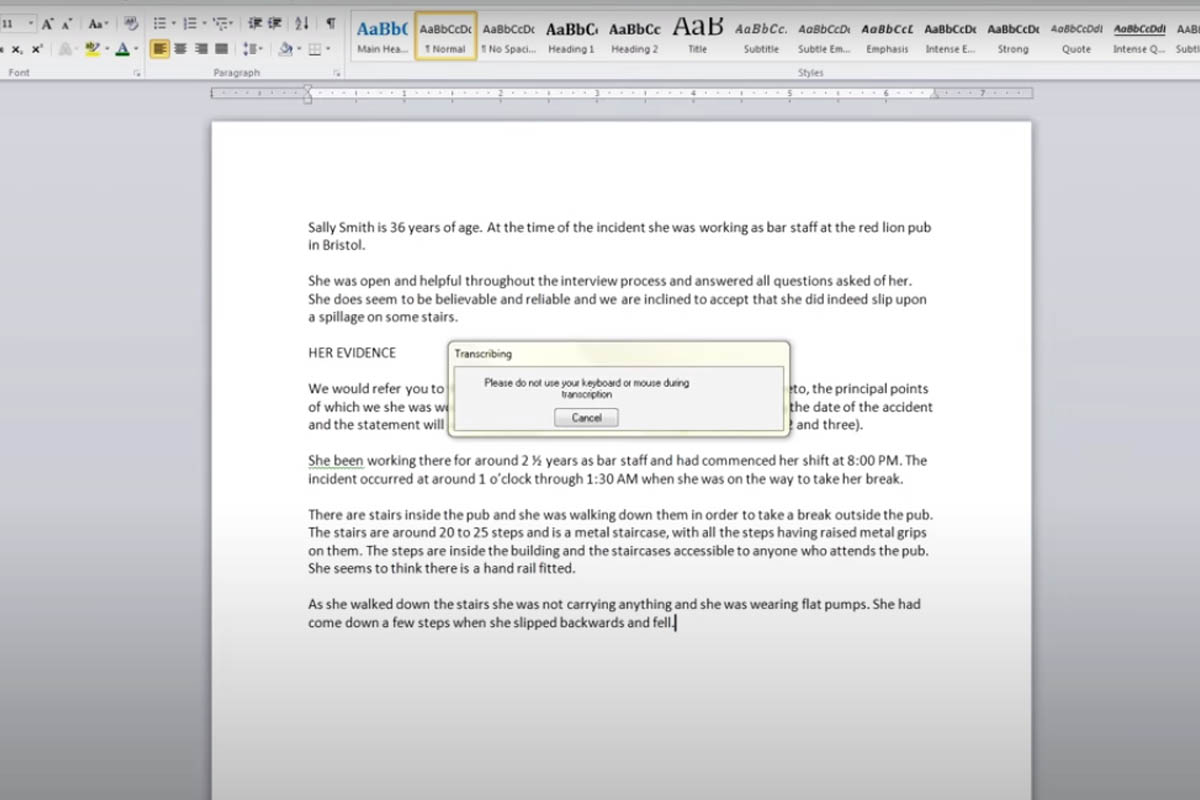
DragonProfessional transcribes audio to text in Word.
Voice Recognition Software Features
While providers offer different features, voice recognition software typically offer the following capabilities:
- Text transcription: A basic voice recognition software lets the user convert speech or audio into a written document or text box.
- Text translation: This feature allows the user to speak in his native language then have it translated to another language.
- Vocabularies: Voice recognition software compares the words it hears to a list of words stored in its vocabulary. The software checks the vocabulary to correct words it might have misheard. Transcripts are also produced by accessing the software’s vocabulary. Some speech-to-text APIs allow you to add individual words or commonly misrecognized words to its vocabulary.
- Automatic playback. A playback option lets the user confirm what was dictated or compare the spoken word with on-screen text. Thus, the user can see mistakes or misrecognized words.
- Commands. The user can speak word strings to launch commands for selecting menus or launching programs. Natural language commands let the user says what he wants in a more flexible, non-robotic way.
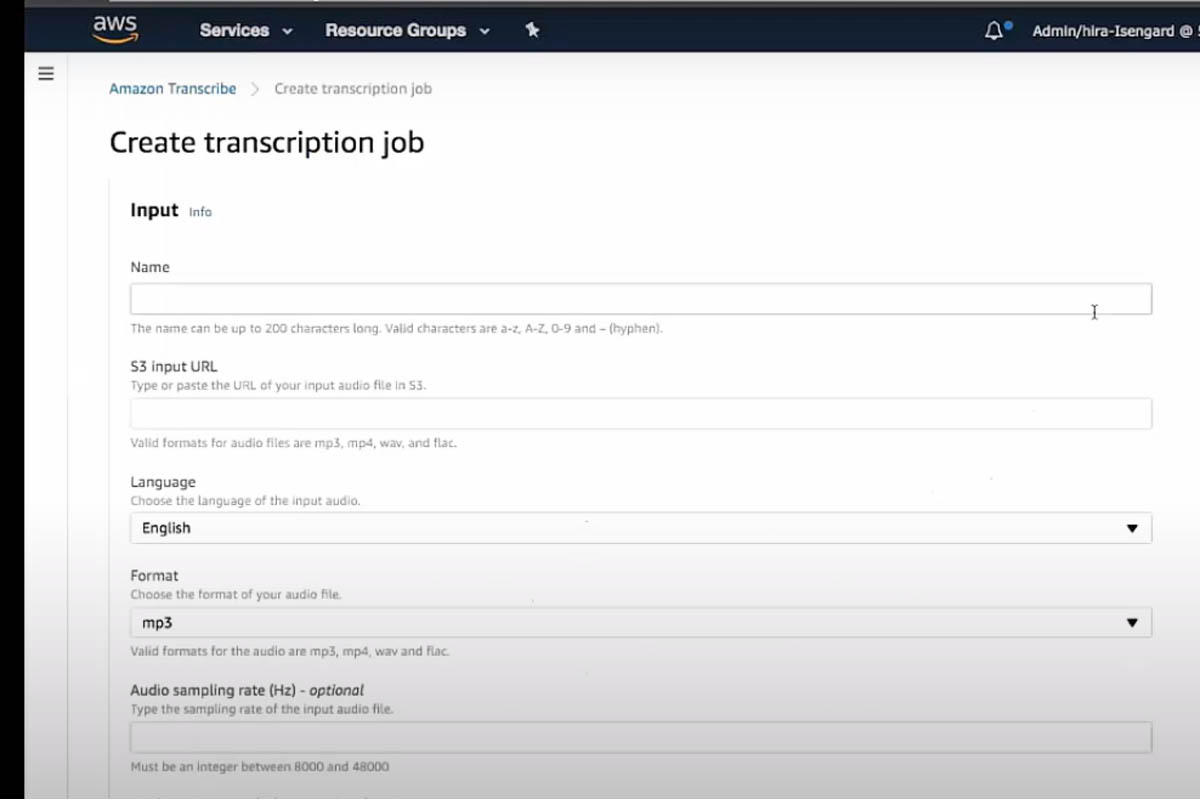
Amazon Translate lets you input data about transcription jobs.
Voice Recognition Software Benefits
Businesses that use voice recognition software can enjoy the following benefits:
- Helps boost productivity. Voice recognition software gets rid of manual transcription so employees can focus on more critical tasks. Through digital dictation, they can send emails, create reports, fill out forms, and accomplish more paperwork in general. Thus, employees spend less time on document-intensive tasks and more time on activities that impact your bottom line.
- Enhance the customer experience. Contact centers can use voice recognition to create a conversational IVR for providing self-service options. Customers can enjoy human-like conversations using a system that does not require human intervention.
- Accessibility compliance. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and Web Content Accessibility Guidelines require closed captioning for people who are deaf or hard of hearing. Businesses producing video content can comply with legal requirements through voice recognition software, which supports this capability.
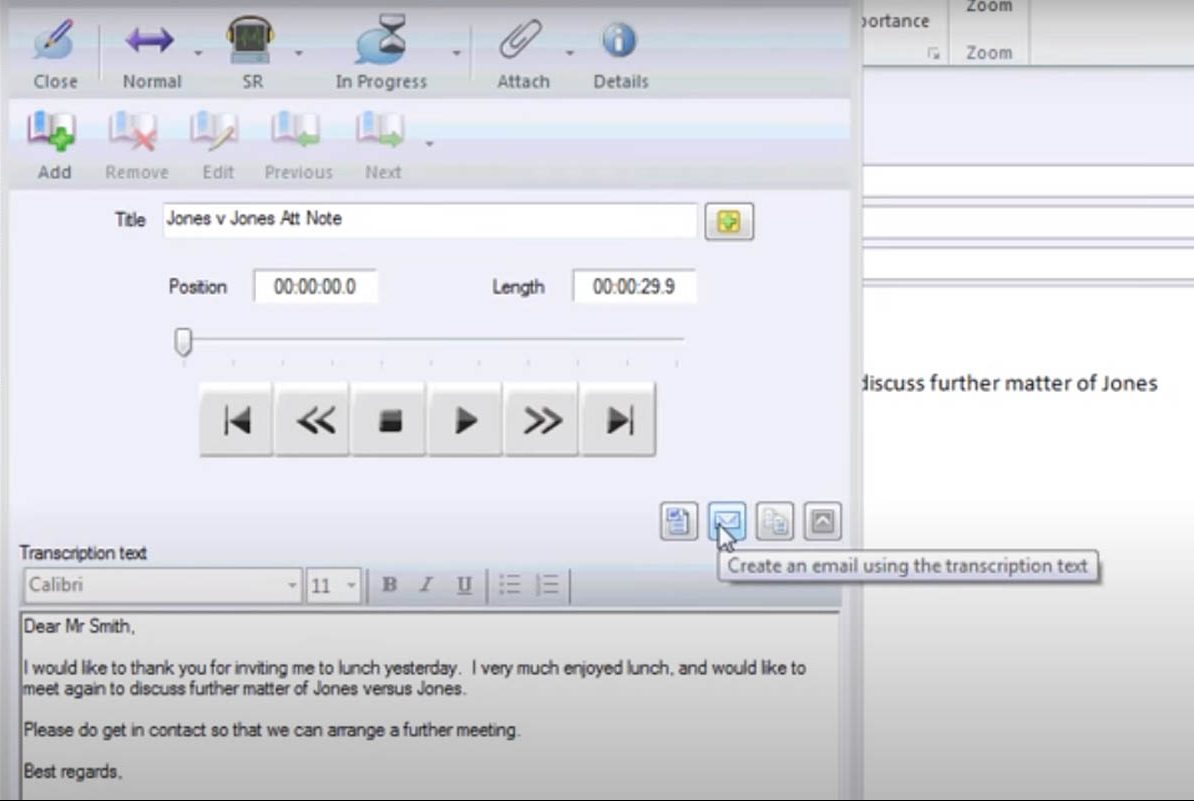
Bighand Professional lets you create emails from transcribed text.
Types of Voice Recognition Software
- Speaker-dependent: Users need to train the software by reading aloud words and phrases. This is used where the software only needs to accurately recognize a limited number of words.
- Speaker-independent: The user does not need to train the software because it is designed to recognize most human voices. It is used in applications where a person doesn’t need to say something to be able to use the system, such as IVR systems.
- Discrete speech recognition: Users must put a distinct pause between every word and command. This is necessary for the software to know when one word stops and another one begins. It tends to be time-consuming and sounds unnatural.
- Continuous speech recognition: Users can speak in a more natural, conversational way. The software can understand utterances in the normal rate of speech.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): The software uses machine learning algorithm to understand spoken language. NLP tools include speech tagging, which lets the software understand the context in which words were used. With NLP, it’s also possible to do sentiment analysis to know the speaker’s attitude towards a certain topic or product.
Voice Recognition Software Trends
- IoT Integration. By 2025, IoT research from Statista indicates that devices connected through the Internet of Things (IoT) will reach 75.44 billion. This represents an opportunity for various manufacturers to add voice capabilities to their products. In the automobile industry, for example, drivers will be able to control the air conditioning thru voice.
- Voice Banking. Leading financial institutions are using conversational AI to manage customer interactions. Today, customers typically use voice to pay for small ecommerce purchases. However, some banks have been introducing voice recognition payments. As voice technology evolves, customers will be more open to using voice for more complex transactions like getting a loan or paying taxes.
- Hyperlocal Search. Fifty-eight percent of US consumers have used voice to look for information about local businesses. According to BrightLocal’s Voice Search for Local Business Study, consumers use voice to get the address, directions, phone number, and operating hours of businesses near them. For retailers, this means optimizing their digital marketing for voice by understanding customer intent.
Potential Issues with Voice Recognition Software
Though it shows great potential, voice recognition software is still in its nascent stages. Thus, the industry is grappling with the following issues:
- Privacy and Data Security. Voice recognition software often involves processing voice data on the cloud. But as a recent Microsoft survey on data protection and privacy shows, businesses have privacy and data security concerns with using cloud-based software. Fifty-three percent of US respondents said that they don’t feel confident that they meet current privacy and data protection requirements. This sentiment stems from the lack of vetting done on cloud-based software for potential privacy and data security issues. In the same survey, 50% of respondents said that they do not evaluate software as a service applications for privacy and data security requirements before they deploy the solution.
- Accuracy. The capabilities of automatic speech recognition to recognize errors have improved in the past five to 10 years. However, voice recognition software has not yet reached a level equal to that of humans when understanding context. This makes it challenging to implement among media companies, which require high levels of accuracy for captioning and subtitling. In fact, 53% of media companies struggle with accuracy issues in speech recognition. As a result, they use a combination of manual and automated processes in their workflows.
- Environmental factors. Voice recognition software work best in quiet environments. Thus, the software might struggle if the user is in a place where there is a lot of background noise. Other people talking at the same time can also cause transcription errors.
Factors to Consider when Looking for Voice Recognition Software
- Check for accuracy. There are voice recognition software companies that boast of high accuracy levels. But as they say, the proof of the pudding is in the eating. Try out the software first to see how error-free your transcriptions are. Some providers offer a free version of the solution with a set number of minutes. To minimize software errors, other vendors complement voice recognition with their own team of human transcriptionists. If so, make sure the provider complies with privacy and data security regulations.
- Think about your users’ speaking environment. If your users are in a busy environment, you might want to look into software that can handle background noise. Other business users might have multiple speakers, in which case you want speaker diarization capabilities. If your recordings involve different channels, you’d want multichannel recognition. For example, in call centers, the recordings involve two channels, one for the agent and the other for the caller. It’s best to look for features that support your particular use case.
- Consider the training needs of your staff and the software. There are dictation software that are ready to use out of the box. However, if you’re building a custom solution for your business, you need to allow time for testing and fine-tuning your model. This is in addition to training your staff to use the software
- Length and number of audio. Typically, business-grade voice recognition software will charge you depending on the length of the audio transcribed per month. Other providers charge a flat fee per transaction within a given range. Figuring out the volume of transcriptions you need will help you predict the costs involved in getting the software.
