We live in a business world where numbers play a more important role than any other factor when determining the success of any business. Every business needs at least 1% of profit from the total amount they spend at the end of the day, which is the ROI (return on investment).
The higher the ROI, the more successful your business is. Although several things influence ROI, one factor that will have a greater impact is your investment in business software.
Using the right business software can be a game-changer for any business. It can improve operations, boost productivity, and lead to increased profits. Yet, investing in business software is not a decision to take lightly.
To make a wise choice, you must understand how to evaluate the return on investment for business software. Do you want to know how you can do that? Read further to find out how you can test the worth of your recent business software purchase.
Understanding the Specific Software Needs of the Business
Before investing your funds in any software, you must understand the specific needs of your business so that your money only goes to necessary business software that solves any of your problems.
This evaluation process involves understanding how your business works, the pain points, and having a clear understanding of the business goals you want to achieve in the next few business years.
The more specific you become about your goals and needs, the more you understand software needs. Always start your evaluation process from the smallest point. Think about your team members or employees who contribute more to the company and your projects. Their insights will help to make an informed decision.
For example,
Let’s take an example: Amazon, a leading e-commerce retailer. After running the business for several months, they understood they needed to improve their inventory management and customer order processing, as these could greatly influence their operations while improving their productivity, customer support, and satisfaction.
So, in evaluating Qualtrics competitor options, taking this decision was only possible through a clear understanding of their pain points for improving efficiency and their long-term goals of improving customer satisfaction. It shows how investing in the right business software could lead to improved success.
In another instance, let’s consider manufacturing businesses. We all know the level of operational complexity that manufacturers face. Their needs are industry specific and it is critical for businesses to explore solutions that can simplify manufacturing processes. Selecting solutions such as MRP software, warehouse management software, delivery solutions etc. are always helpful.
Calculating the Upfront Costs of Software Acquisition
Once you identify all the specific needs of your business, it is high time that you choose software by calculating the costs that come with buying and implementing it in your systems.
These costs can include software licenses, hardware upgrades, and consulting fees. The prices vary from software to software and location to location. So, contact the nearest software vendors and service providers for an estimated cost for a specific one.
When calculating costs, remember to consider the long-term factors. Are there ongoing subscription fees or maintenance costs? Also, training your team should be part of your budget. Your employees need proper training so they can use the tool to get the most out of it.
How to Evaluate the ROI for Your Software Investment?
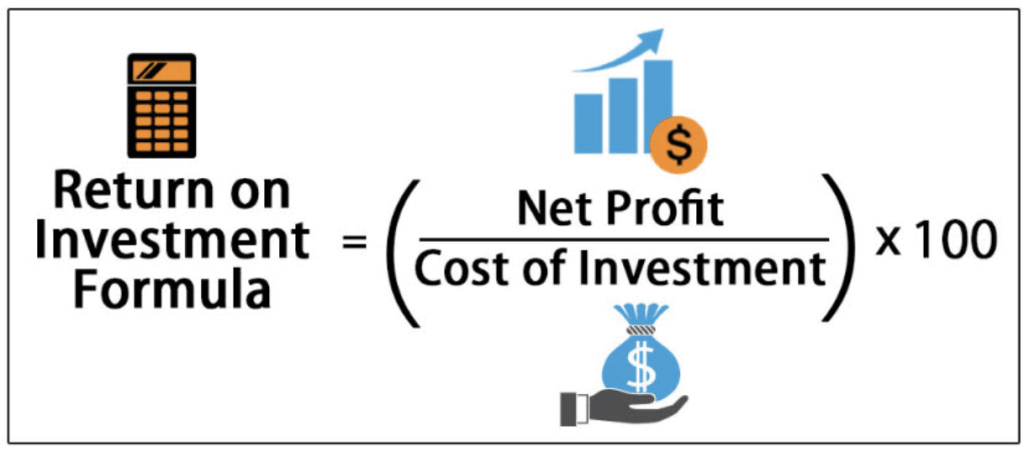
The heart of the matter is calculating software ROI. ROI (return on investment) is a metric that tells you whether your investment in business software is worth it.
The ROI formula is simple yet effective.
ROI = (Net Gain / Investment Cost) x 100.
Net gain/profit represents the financial benefits you get from the software, such as increased sales, reduced operational costs, or improved efficiency. The investment cost contains all the other expenses, such as software purchases, hardware, and training.
Suppose,
The e-commerce platform, Myntra, purchased a customer relationship management (CRM) software solution for $100,000.
Over the following two years, Myntra saved $250,000 on production costs and improved supply chain management using this software.
You can calculate the ROI using the formula:
ROI = (($250,000 / $100,000) x 100) = 150%
In this case, Myntra achieved a 150% ROI on its software investment.
Now, let’s break down the components of the ROI formula in more detail.
1. Net Gain/Profit
It shows the positive impact the software has on your business. It might be challenging to predict accurately, but proper market research and past performance data from various business reviews can help you make a reasonable estimation.
2. Cost of Investment
The investment cost is the total money you spend on the software. It includes the purchase, implementation, training, and other external expenses.
Be sure to add all costs to get an accurate ROI percentage.
3. Multiply by 100
Multiplying by 100 to the total divided by the value gives the ROI percentage.
This step is crucial as it shows the exact ROI, and you can use this information to compare various investments and make informed decisions going further.
Evaluating the Impact of Risk on ROI
Evaluating software investment risks when investing in business software is something that you can’t ignore. The risk can come in various forms, from software not meeting your expectations to technical issues that do not improve your efficiency and changing market conditions.
These uncertainties, even if they are minor, can affect your ROI. So, here are a few things to help you with this.
1. Risk Assessment
You must identify potential risks in the software investment, including technical challenges, market changes, or vendor reliability. It is possible to prepare for risks by being aware of them.
For example, the software you use today might become outdated tomorrow, so you can take the necessary precautions beforehand to avoid any risks.
2. Risk Mitigation
Once you know the risks you might face, develop a plan to minimize them. You can negotiate contractual terms with the software seller or implement backup solutions.
For instance, you can do a sample through testing before introducing the business software into your operations.
3. Risk Contingency
The advantage of having multiple solutions to a problem is that you can go from one to another if one does not work as expected. It can include setting extra money aside or having alternative plans.
For example, you can go to plan B of software at a cheaper price if plan A of buying an expensive one does not work.
4. Regular Monitoring
After implementing the software, keep a close eye on its performance. Monitor it regularly, while periodic reviews will help you identify and address any issues promptly.
For instance, the software you purchased may or may not improve your work efficiency, so it is important to monitor its performance.
Conclusion
Investing in business software can yield better returns only when you choose the platform wisely. It is not about choosing it in one go; it involves more than that, from studying the problem to relating the software to your needs and goals.
Calculating software ROI is one way you can measure the overall success rate of your chosen software. The ROI formula, which is simple yet effective, allows you to analyze the financial impact of your investment.
Tracking the return on investment for business software and evaluating software investment risks are two tasks you should never compromise on. It is not just about technology. It is about aligning your software choices with your business goals.