Developing a new product is a complex process that requires careful planning and execution, from ideation to production. Between the excitement of a new idea and launching the final product, certain critical processes make up the product development life cycle. Each stage of this cycle plays a vital role in shaping the outcome of the product.
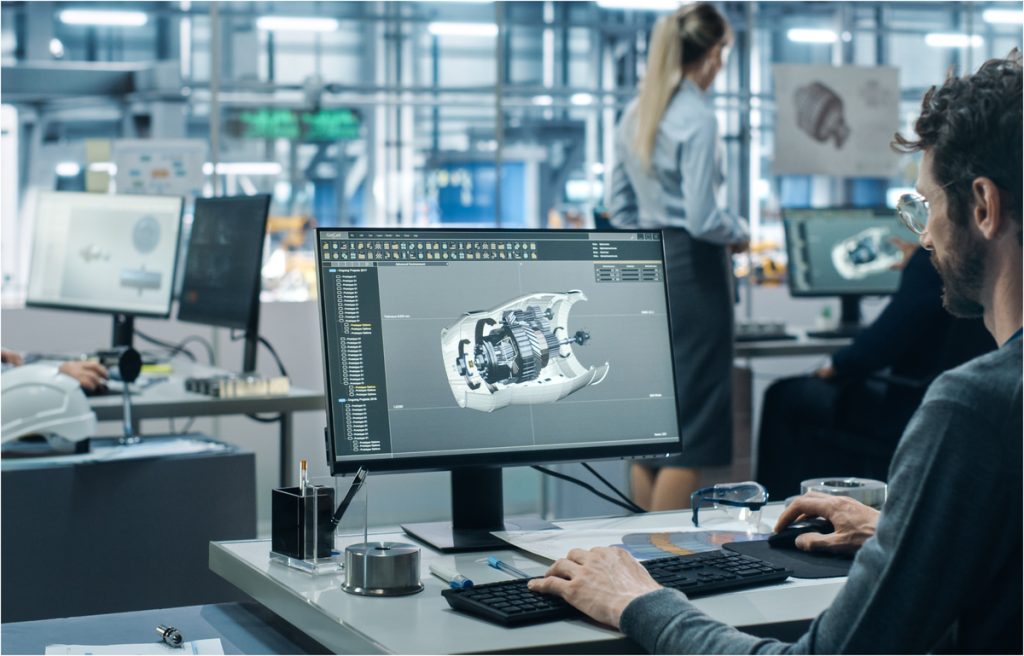
The design and prototyping stages are vital to successful product development as they help you plan and test the product before the actual execution and release. With proper prototyping using powerful design prototyping solutions, SaaS or On-Premise, your company can be sure the product/concept matches its expectations and desired result before releasing it to the public.
Let’s explore what design and prototyping entail and why it is the foundation for a successful product.
What is Product Development?
Product development summarizes all the processes involved in creating new products from start to finish. It also involves revamping existing products to meet current market standards or demands, or launching an old product in a new market.
A successful product development campaign achieves two primary purposes: to ensure that the product is valuable and meets required quality standards, and to satisfy customer demand, thereby increasing the company’s market share.
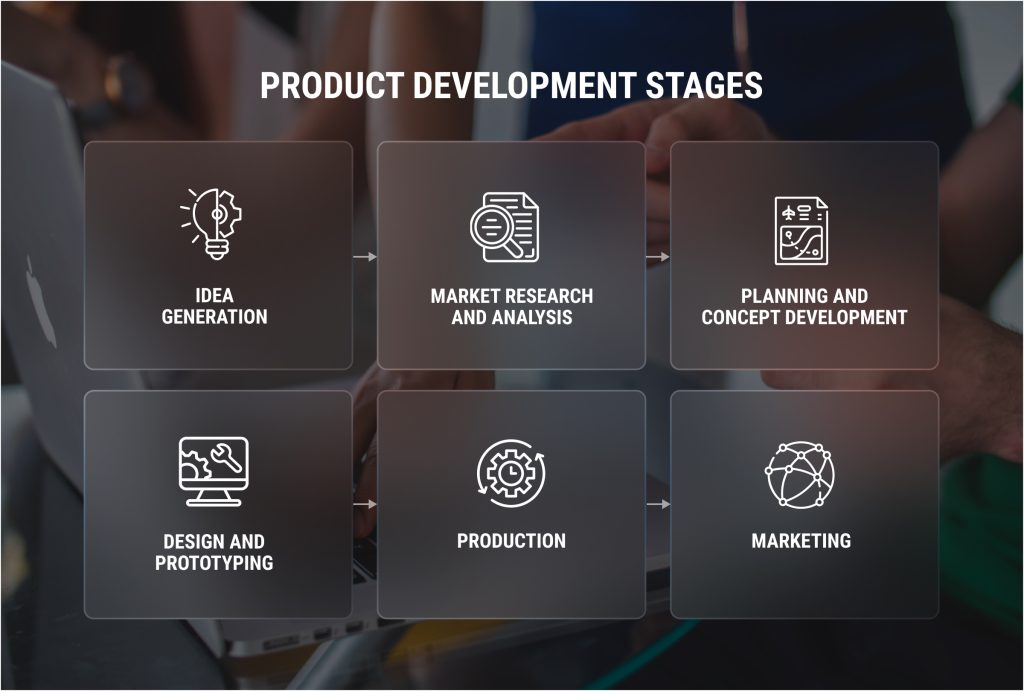
Stages of product development
The stages of a product development cycle may vary across different companies, both in procedures and in sequence. However, typical product development should include the following processes:
- Idea Generation: Identifies the problem and proposes a possible solution.
- Market Research and Analysis: Determines product viability, defines the target market, identifies and analyzes competitors, etc.
- Planning and Concept Development: Creates the product roadmap and defines features and functionalities in their respective order.
- Design and prototyping: The heartbeat of the product development process. While design visualizes the concept for better presentation and interpretation, prototyping brings the product to life for testing.
- Production: Creation of market-ready products based on design and prototyping.
- Marketing: Summarizes the processes involved in getting the finished product to the market.
While each stage is critical to a new product’s success, the design and prototyping stage sits at the heart of the cycle, bridging the gap between ideation and full implementation. Let’s delve into more details on design and prototyping and why they’re essential in product development.
What is Design and Prototyping in Product Development?
Design in product development refers to conceptualizing and visualizing a product to illustrate its features, functionalities, appearance, and user experience. The design phase focuses on defining the look and feel of a product as well as the user interactions.
The design process could start with simple hand-drawn sketches and advance to sophisticated wireframes and 3D drawings containing details that guide the development team. What’s important is that it’s as detailed as possible, with appropriate labels explaining the important components of the product.
Prototyping in product development involves building a tangible model or sample representing the designed product. Prototypes can either be physical or digital. For instance, builders can construct a model house with paper or other inexpensive materials to prototype the architectural design of a house. Similarly, app developers can build a prototype app to simulate their product.
Note that prototypes can come in different levels and stages to help designers and product owners interact with different stages of the product.
Types of Design Prototyping and Software Tools
Prototypes serve different purposes and allow businesses to test and refine their concepts before proceeding to full-scale production. Some common types of design prototypes are described here.
Low-fidelity prototypes
Low-fidelity prototypes are simple and basic representations of a product idea. They are often created using inexpensive materials like paper, cardboard, or digital wireframes. Their easy-to-produce nature makes them suitable for gathering initial feedback from stakeholders and potential users.
High-fidelity prototypes
High-fidelity prototypes are more detailed representations that closely match the final product in appearance and functionality. They are created using more sophisticated materials and techniques, such as 3D printing or CAD software. They provide a more realistic user experience and are suitable for in-depth usability testing and gathering comprehensive feedback.
Interactive prototypes
Interactive prototypes simulate the user experience, enabling businesses to test the product’s features and functionalities in a more dynamic and engaging manner. They are particularly valuable for user testing and validating user interfaces.
Virtual prototypes
Virtual prototypes are digital models and simulations of a product, often created using CAD or computer-aided engineering (CAE) software. Most virtual prototyping software integrate both CAD and simulation capabilities, enabling companies to create highly detailed virtual prototypes. Examples of such SaaS solutions include Autodesk Fusion 360, SolidWorks, and Ansys.
Virtual prototypes are especially useful for complex products like machinery, buildings, or vehicles, where physical prototypes may be impractical or costly. According to a survey report by Solidworks, 67% of top-performing companies rely on virtual prototyping SaaS software for design validation and verification. For instance, top automotive manufacturers like Ford and Toyota embrace virtual prototyping to reduce development costs and time.
Functional prototypes
Functional prototypes are working models that demonstrate the core functionalities of the product. Beyond visual representation, they perform the intended tasks. Functional prototypes are crucial for testing the technical and performance aspects of products.
Aesthetic prototypes
Aesthetic prototypes focus on the product’s appearance and design elements and might not include functional components. They are mostly used in industries such as fashion, industrial design, and consumer electronics.
The Role of Design Prototyping in Product Development
Design prototyping provides numerous benefits that contribute to the overall success of a product. Here are some of the key components of design prototyping in product development.
Visualization and concept validation
Design prototyping allows designers and stakeholders to visualize and interact with product concepts in a tangible form. By seeing a physical or digital prototype, stakeholders can better understand the product’s features, aesthetics, and functionality. This helps validate and refine design ideas, ensuring they align with the intended vision and purpose of the product.
User-focused development
Designers gather direct feedback from potential users by creating prototypes and involving users in usability testing. This feedback helps identify user preferences, usability issues, and pain points early in the design process.
User-focused development helps companies improve customer satisfaction and, consequently, gain more customer loyalty. A study by Adobe reveals that 50% of user-focused, design-led companies report more loyal customers, while 46% report a competitive advantage.
Iterative improvement
Instead of depending entirely on theoretical assumptions, designers can test multiple iterations of a product concept. That way, they can continuously improve on the product, as each prototype iteration provides valuable insights for refinement.
Risk mitigation
By testing and validating prototypes, designers can identify and address potential risks associated with product development and user acceptance, such as design flaws, technical challenges, and usability issues. Addressing these challenges early in the design phase saves time and resources in the long run.
Cost-efficient production
Iterative prototyping helps companies continuously tweak the product design and its functionalities until it perfectly matches the intended product. This helps reduce the likelihood of expensive rework and product recalls, optimizing resources and ultimately leading to cost-efficient development.
Faster time to market
Rapid prototyping techniques allow designers to create quick iterations and validate design concepts in a shorter time frame. This efficiency enables businesses to respond to market demands more quickly and gain a competitive edge.
Top 7 Best Practices For Design Prototyping
Start early in the design process
Early prototypes help validate and refine initial concepts, allowing you to identify potential design flaws and usability issues before investing significant resources.
Set clear objectives
Each prototype should have clear objectives and goals. Understand what specific aspects of the product you want to test or validate with each iteration. Having clear objectives helps create focused and meaningful prototypes.
Focus on user-centric design
Gather feedback from potential users through usability testing and incorporate their insights into the design. Prioritize user needs and preferences to create a product that resonates with the target audience. You can leverage SAP Customer Data solution and other powerful SaaS customer support software to gather, organize, and manage user feedback.
Use the right tools
Choose prototyping tools that best fit your needs and the complexity of the product. The right tools speed up the process and enhance the prototypes’ accuracy and effectiveness, leading to a smoother transition from concept to product. According to a report by SolidWorks, companies that use virtual prototyping tools reduce their overall development time for new products by 13%.
Most top-class companies prefer SaaS CAD tools over traditional software for a variety of reasons. With SaaS tools running on the Cloud, collaboration is easy for the product development team as multiple teams and users can access and edit the design simultaneously. Also, SaaS tools offer subscription-based pricing, which can help reduce upfront costs and provide scalability options.
Various SaaS and On-Premise software are available for digital prototyping, as well as traditional tools like paper and cardboard for low-fidelity prototyping. Your choice of tool depends on the complexity of the project and the specific needs of your organization.
For instance, you can explore the SAP Visual Enterprise Generator (VEG) to translate 3D CAD files into lightweight formats that you can share throughout your organization. Use the SAP Visual Enterprise Author to create 3D animations. Other common tools for design prototyping include Figma, Adobe XD, Sketch for macOS, etc.
Test real-world scenarios
Consider how real-world users will interact with the product in different contexts and environments. This approach helps identify potential challenges and optimizes the product’s usability.
Balance fidelity
Use the appropriate level of fidelity, or reliability, for each stage of the design process. Low-fidelity prototypes are great for early validation, while high-fidelity prototypes are ideal for detailed testing and presentation to stakeholders.
Document and communicate
Proper documentation ensures continuity and clarity throughout the development process. Communicate the findings and insights gathered from prototypes to all relevant stakeholders. Also, ensure to keep the documents safe for future reference. You can leverage the robust SAP DMS or other document management software to create, organize, share, and store your documents safely.
Final Thoughts
Design prototyping is critical to successful product development, from visualizing and validating design concepts to saving time and resources. With the right tools and adherence to prototyping best practices, companies can be sure their products are up to the best standards before releasing them to the market.